If you ask your lawn care professional whether they prefer organic or chemical fertilizer, chances are you’ll hear a variety of responses. If you could ask your lawn the same question, you’d find out that at the most basic level, it can’t tell the difference between organic fertilizers and chemical fertilizers – nutrients are nutrients. However, when it comes to the soil health there are major differences between organic and chemical fertilizers.
Professional lawn care companies describe their products as organic, natural, inorganic, chemical, synthetic, artificial, organic based, and manufactured. But what do these mean for you as the consumer? We are going to reduce these terms to reveal whether they are organic fertilizers or synthetic fertilizers.

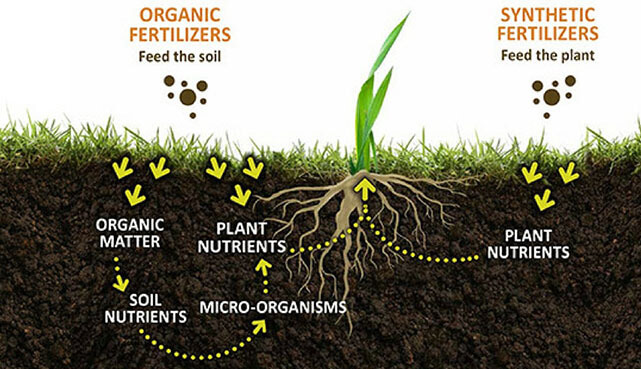

Organic Fertilizers
If you see the term organic fertilizers, or sometimes referred to as natural fertilizers, this means that the end product is minimally processed and the nutrients remain in their natural forms. The raw materials need to be decomposed by microbial activity prior to the nutrients being converted into a form that plants can uptake.In the case of lawn fertilizers, organic does not refer to the same standards of processing associated with food. Organic fertilizer is typically derived from plant or animal waste. Examples include: corn gluten meal, bone meal, sugar beet molasses, or animal manure. Organo-Lawn prefers to use plant-based products instead of manure based organic fertilizers because plant-based products are more consistent than animal-waste fertilizers.
Advantages of Organic Fertilizer
- In addition to releasing nutrients, organic fertilizers are broken down by the microbial activity in the soil and will improve the structure of the soil. This increases the soil’s ability to hold water and nutrients. If used regularly with proper lawn watering and mowing, organic fertilizers will make your soil and grass healthy and strong.
- Organic fertilizers will only release nutrients (like nitrogen, phosphorous, and potassium) as the microbes consume and convert them into a form that the plant can uptake.This process makes it impossible to burn a lawn when using a truly organic fertilizer.
- There’s no risk of toxic buildups of salts when using organic fertilizers that can be deadly to plants.
- Organic fertilizers are renewable, biodegradable, sustainable, and environmentally friendly.
- Organic fertilizers not only feed the grass and plants, but they also feed microorganisms in the soil. Soils teeming with microorganisms are called living soils, and these microorganisms build and sustain nutrient levels in the soil.
- During hot summer days or colder temperatures in the winter, the microorganism activity is reduced. In these times of reduced activity, the availability of nitrogen is less abundant, protecting the plant life from excessive nitrogen exposure during stressful heat or extreme cold.
- The symbiotic relationship between microorganisms and organic fertilizers is incredible. The microorganisms create a living soil, which is a naturally controlled-release nitrogen source, which prevents lawn diseases and will not cause excessive growth.

Disadvantages of Organic Fertilizer
- Microorganisms are required to break down the organic components before the nutrients are released into the soil. Since microbes need warmth and moisture to do their job, the effectiveness of organic fertilizer is limited by these factors.
- Organic fertilizers require the presence of microorganisms to work.If a soil is dead and is lacking microbial activity due to many years of chemical fertilizer applications, the time it will take to show visual improvement will be slow compared to a chemical fertilizer application.As the microbial population reestablish their populations the organic fertilizers will be more effective faster.
- In the beginning, patience is required with organic fertilizers. In fact, when transitioning from a chemically dependent lawn to an organic lawn you may actually see a deficiency in your plants health during the first couple of months until the microbes fully establish themselves. Be patient! You’ll most definitely be rewarded.
Chemical Fertilizers
Chemical fertilizers, otherwise called inorganic, synthetic, artificial, organic based, or manufactured fertilizers, have been refined to extract nutrients and bind them in specific ratios with chemical fillers. These products are often derived from petroleum products, rocks, or other sources. The nutrients in chemical fertilizers are refined to their purest state and stripped of substances that control their availability to breakdown.Therefore, the nutrients in chemical fertilizers are typically readily available for uptake by the plant without the need for microbial activity in the soil.
Advantages of Chemical Fertilizer
- Since chemical fertilizers are typically refined to be fast-release nutrient sources, the nutrients are available to the plants immediately and plants will show improvement quickly.
- Chemical fertilizers are inexpensive.
Disadvantages of Chemical Fertilizer
- Chemical fertilizers are typically made from nonrenewable sources, including fossil fuels and petroleum products.
- Chemical fertilizers kill microbes in the soil.Most chemical fertilizers are refined salt, and these high concentrations of salt are extremely toxic to beneficial microbial activity in soils.
- Chemical fertilizers lack organic matter.Trace elements in the soil are gradually depleted, resulting in long-term damage to the soil.
- The nutrients, especially nitrogen, are readily available to the plant for uptake.Therefore, there is a high risk of burning a lawn if the fertilizer is over applied. This not only kills plants, but upsets the entire soil’s ecosystem.
- Chemical fertilizers tend to leach from the soil, especially with over irrigation.The fertilizer is wasted and often washed into lakes, rivers, ponds and oceans where algae populations can become extreme.
- Synthetic lawn care fertilizers can green up a lawn very quickly, but the dark green color fades almost as quickly as it developed. To sustain a green lawn with synthetic fertilizers, frequent applications of fertilizer are required. If applications cease, the lawn will fade to a pale green or yellow because the synthetic fertilizers have caused the soil to die.



